Barcodes, a common sight in our daily lives, are machine-readable symbols that represent data visually. Introduced in the 1970s, barcoding has become an integral part of commercial transactions. A barcode is a series of parallel bars or lines of varying width, typically black on a white background. They are found on product packages in supermarkets, convenience stores, and other retail outlets. These barcodes, consisting of varying widths of bars and spaces, can be verified for GS1 India Authenticity. This verification process helps ensure the product you’re purchasing is genuine and combats counterfeiting. They can be read with an optical barcode scanner. This data is entered into a computer system using an optical (laser) scanner. The scanner, either handheld or built into a checkout counter, reads the barcode by moving across the code or having the code moved across it.
GS1 barcodes
The GS1 system of standards aims to raise the efficiency of business processes and to provide cost savings through automation based on globally unique identification. The GS1 barcodes system provides globally unique and unambiguous identification keys to identify goods, services, assets, locations, etc.. These keys can be represented in data carriers, such as barcodes or EPC/RFID tags, to enable automatic data capture. They may also be used in electronic communications, improving speed and accuracy when sharing master data, transactional data and visibility event data.
GS1 barcodes are designed to overcome the limitations of using company’s, organization’s, or sector-specific interfaces. It enables large scale deployment, flexibility in the selection of the most suitable system components and innovation − ultimately making trade much more efficient and responsive to customers. GS1 barcodes are designed for use in any industry or trade sector, and changes to the system are introduced in a way that does not disrupt existing users.
Understanding the GS1 Barcode System
Overview of GS1
GS1 is a global supply chain standards organisation that develops and maintains global standards. It is linked to the issuance and maintenance of barcodes, a symbol printed on products that can be scanned electronically. GS1 barcodes are scanned more than ten billion times every day, making them one of the most widely used information systems in the world.
It has a crucial role in the standardization of barcodes as it provides a common language that ensures key processes run smoothly wherever they happen. GS1 standards bring together companies representing all stakeholders of the supply chain or regulatory authorities – manufacturers, distributors, retailers, transporters, customs , software developers, and more. GS1 standards are designed to improve the efficiency, safety, and visibility of supply chains across physical and digital channels in various sectors. They form a business language that identifies, captures, and shares key information about products, locations, assets, and more.
GS1 role in Standardizing Barcodes
The role of GS1 in standardizing barcodes involves several aspects. GS1 develops standards based on industry global best practices. These standards provide a framework that allows products, services, and information to move efficiently and securely, providing visibility and traceability for businesses and their customers.
GS1 assigns unique identification numbers to companies for use in their barcodes. These numbers are globally unique and ensure that every product can be identified in the supply chain. They promote the use of its standards and barcodes across industries. It also provides training and resources to help businesses implement and use these standards effectively. They also plays a role in ensuring that companies comply with its standards. It provides tools and guidelines to help businesses meet these standards and maintains a database of companies that are in compliance.
GS1 plays a pivotal role in standardizing barcodes, ensuring that they can be used effectively and consistently across different industries and countries. This standardization is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and integrity of global supply chains.
Explanation of GS1 Barcode Structure and Encoding
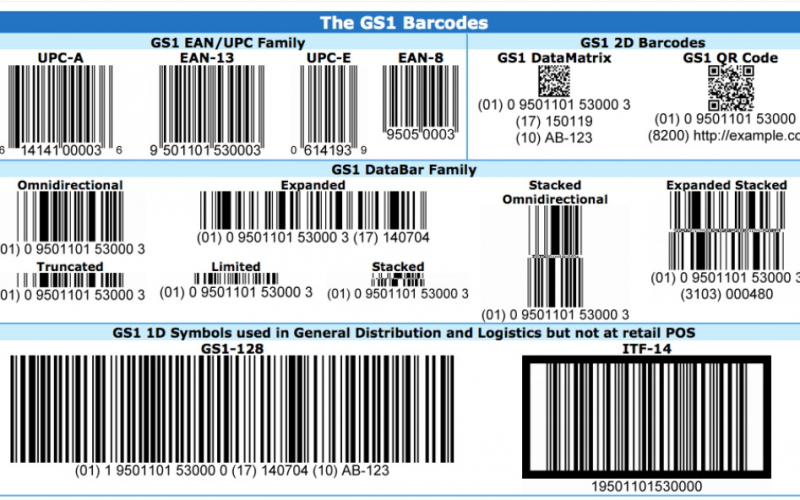
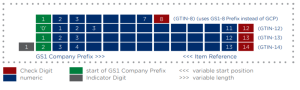
GS1 barcodes are structured to contain a series of digits that are encoded in a sequence of bars and spaces. Each digit from 0 to 9 is represented by a unique pattern of bars and spaces. The structure of a GS1 barcode includes a GS1 Company Prefix, an Item Reference, and a Check Digit. The GS1 Company Prefix is assigned by GS1 to a company, allowing it to identify its products globally. The Item Reference is assigned by the company to each of its products. The Check Digit is a calculated one-digit number used to ensure data integrity. To read the barcode, the scanner decodes the pattern of bars and spaces to extract the digits and interpret the information.
Importance of GS1 India Authenticity in Barcodes
How GS1 India Authenticity Ensures Global Uniqueness
Authenticity is a key feature of GS1 barcodes as it ensures the global uniqueness of each barcode. This is achieved through the GS1 Company Prefix, which is a unique identifier assigned to each company by GS1. This prefix, when combined with the Item Reference and Check Digit, creates a globally unique identifier for each product. This system prevents duplication of barcodes, ensuring that each barcode is authentic and traceable back to its original source.
Benefits of Using GS1 Barcodes for Businesses
GS1 standards provide unique identification for products, locations, which forms the backbone on which applications such as track and trace , product authentication, and product recalls are built. GS1 standards are interoperable and technology agnostic making them independent of Hardware /software platforms and technology solutions.
They facilitate efficient inventory management by enabling quick and accurate scanning of products. They also support global trade by providing a common language that businesses around the world can understand. GS1 barcodes help in reducing errors in data entry and retrieval, thereby improving operational efficiency. They also play a crucial role in fighting counterfeit products by ensuring the authenticity and traceability of products. By adopting GS1 barcodes, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and protect their brand reputation.
The use of GS1 barcodes is a proactive step towards ensuring the authenticity of products and protecting business from counterfeiters. It is critical to stay informed in order to stay protected!
Rising Concerns: Scammers and Fraudulent Barcode Companies
The Increasing Prevalence of Barcode Scams
In the digital age, the prevalence of barcode scams has seen a significant increase. Unscrupulous entities exploit the trust of businesses, selling them counterfeit barcodes that are not registered with GS1. This not only leads to serious consequences for businesses but also disrupts the integrity of global trade systems.
Common Tactics Used by Fraud Companies
Fraudulent companies often employ deceptive tactics to lure unsuspecting businesses. They offer non-authorized barcodes, claiming that these barcodes are GS1 compliant. However, these barcodes are not registered with GS1 and hence, do not provide the benefits of GS1 India authenticity.
Identifying Genuine GS1 Barcodes
Guidance on verifying GS1 India authenticity
GS1 provides tools to verify the authenticity of its barcodes. One such tool is the GS1 VBG (Verified by GS1). By entering the barcode number into this tool, businesses can check the validity of a GS1 barcode, ensuring it is not a fake.
Tips for Businesses to Ensure They Are Dealing with Legitimate GS1 Codes
To ensure they are dealing with legitimate GS1 codes, businesses should always purchase barcodes directly from GS1. Regular checks using the GS1 GEPIR tool can help verify the authenticity of the barcodes.
The Consequences of Dealing with Fraudulent Barcodes
Legal Repercussions for Businesses Using Fake Barcodes
The use of fake barcodes can lead to legal repercussions for businesses and impact brand reputation for your business. These can range from fines and penalties to lawsuits. Moreover, the use of counterfeit barcodes can damage a company’s reputation and lead to a loss of customer trust.
Impact on Supply Chain and Customer Trust
Counterfeit barcodes can have a significant impact on the supply chain. They can lead to incorrect data being captured, resulting in stock discrepancies and delivery errors. This not only disrupts the supply chain but also erodes customer trust.
How to Spot Scammers: Red Flags and Warning Signs
Signs That a Company May Be Selling Counterfeit Barcodes
There are several red flags that can indicate a company may be selling counterfeit barcodes. These include unusually low prices, lack of GS1 authorization, and inability to provide proof of GS1 registration.
Case Studies or Examples of Fraudulent Barcode Transactions
While specific case studies are confidential, there have been instances where businesses have faced significant losses due to the use of counterfeit barcodes. These cases underscore the importance of GS1 India authenticity.
Reporting Scams and Protecting Your Business
Steps to Take If You Suspect a Barcode Scam
If a business suspects a barcode scam, it should report the matter to GS1 India immediately. It should also cease using the suspected fake barcodes and replace them with authentic GS1 barcodes.
Advice on Safeguarding Your Business Against Fraudulent Transactions
To safeguard against fraudulent transactions, businesses should always purchase barcodes from GS1 India. Regular checks using GS1 GEPIR app or Smart Consumer app can help verify the authenticity of the barcodes.
Conclusion
GS1 India authenticity is crucial for the smooth functioning of global trade systems. It ensures the global uniqueness of barcodes on their products, facilitates efficient business operations, and protects against counterfeit barcodes.
Businesses should remain vigilant against barcode scams and report any suspicious activity to GS1. By staying informed and proactive, businesses can protect themselves and contribute to the fight against barcode fraud.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are barcode number unauthorized sellers?
Unauthorized sellers are those who sell products without the necessary permissions or approvals from the brand or manufacturer. They typically operate outside the official distribution channels set up by the brand and often acquire products through unauthorized means.
2. What happens if I buy barcode numbers from an unauthorized seller?
Purchasing barcode numbers from an unauthorized seller can lead to a variety of issues. These can include legal disputes, inability to sell the product due to duplicate numbers, damage to brand image and reputation, and potential difficulties in listing on e-commerce platforms.
3. Where can I get legitimate GS1 barcode numbers?
You can obtain legitimate GS1 barcode numbers from GS1 India which is a member organization of GS1 global.
4. What is the difference between GS1 issued barcodes and barcodes from 3rd party sources? Why use GS1 barcodes instead of 3rd party alternatives?
GS1 barcodes are globally recognized and used by companies worldwide. They are unique, accurate, and adhere to current global standards. In contrast, barcodes from 3rd party sources may not be globally recognized and can lead to confusion and inaccuracies.
5. What does GTIN Non-Reuse Standard mean?
The GTIN Non-Reuse Standard implies that a GTIN assigned to a trade item should not be reassigned to another trade item.
6. Why is the need for a GTIN Non-Reuse Standard?
The GTIN Non-Reuse Standard is necessary to ensure that product identifiers are permanent and unique. This supports seamless consumer experiences across various channels.
7. What does it mean to the industries?
The GTIN Non-Reuse Standard helps industries maintain unique product identification, which is crucial for maintaining operational efficiencies and ensuring smooth operations of global supply chains.
8. Does the GTIN Non-Reuse Standard apply to all levels of the packaging hierarchy?
Yes, the GTIN Non-Reuse Standard applies to all trade items in the assigned packaging hierarchy, regardless of the sector.
9. Why individual GTINs can’t be reused?
Individual GTINs can’t be reused because reuse can create confusion online where products have a permanent presence. It can result in inaccurate catalogue data, and make GTIN management unclear for brands with products in multiple sectors.