
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses radio waves to transmit data encoded in tags. While both barcodes and RFID are used for product identification, RFID takes it a step further as it enables the unique identification of individual objects through the use of tags. This cutting-edge technology plays a critical role in supply chains, with its application depending on a company's specific needs. In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of RFID, delve into its usability, understand how it enhances transparency, and examine real-world applications with the help of a case study.
RFID tags use electromagnetic fields to transmit data from a data carrier to the receiver. They are small electronic devices that store data on a product and communicate by sharing this information through radio waves. RFID tags can be read, and encoded data can be shared without direct contact. This is extremely crucial when goods need to be tracked and traced. Let’s take a closer look at the components of RFID technology -
RFID Tags: A tag can be any object capable of storing data and sharing information. It contains a microchip and antenna, both serving different purposes. A microchip encodes data, and an antenna acts as a bridge between the microchip and the reader to transmit information encoded in it. There are 3 types of RFID Tags -
Passive RFID Tags: These tags do not have their own power source. They rely on the radio waves emitted by the reader to power the tag and send back information. Passive tags are more affordable and commonly used in applications like inventory management and supply chain tracking.
Active RFID Tags: These tags have a power source (typically a battery) that allows them to broadcast signals over longer distances. Active tags are typically used in applications requiring longer read ranges, such as vehicle tracking or asset management.
Semi-Passive RFID Tags: Also known as battery-assisted passive tags, these tags have a battery to power the tag's internal circuitry but still rely on the reader’s signal to transmit data. They have features of both passive and active tags.
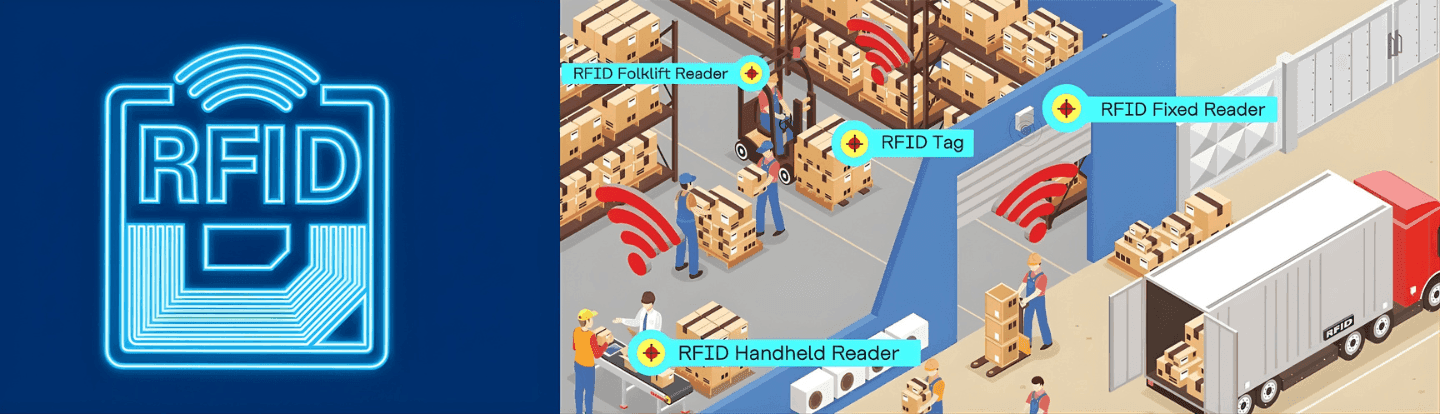
RFID Reader (Interrogator): It is the device that emits radio waves to communicate with tags at a distance, retrieves the information encoded in the tag, and stores it.
Types of Readers: Fixed Readers: These are stationary devices that are installed in specific locations, like a warehouse door or a gate. Fixed readers are commonly used in inventory management, access control, or toll collection.
Handheld Readers: Compact, portable devices used for manual scanning, often used for inventory counts or equipment tracking.
RFID Middleware: It is a software that connects RFID hardware/objects to business applications. It stores the data collected by an RFID reader and transports that by providing an application-level interface.
RFID technology plays a crucial role in powering supply chain visibility. Below are some reasons why -
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) is responsible for the development, maintenance, and management of highways in India. The NHAI, jointly with its concessionaires and financial institutions, incorporated the Indian Highways Management Company Limited (IHMCL) on 26 December 2012, to implement electronic tolling. In 2014, it introduced FASTag as a pilot project to streamline electronic toll collection, reduce congestion at toll plazas, and promote a more efficient and digitised transportation system. By the end of 2019, its implementation was made compulsory for all vehicles.
FASTag is an RFID tag that has a microchip installed for quick toll deduction at toll plazas. It is attached to the vehicle’s windscreen to facilitate fast and easy toll collection. Each FASTag encodes an EPC (Electronic Product Code). The GIAI-96 coding scheme is used for encoding in the EPC memory of RFID tags on vehicles. The IHMCL has obtained GCP from GS1 India to maintain the unique ID data format used for the FASTag program. The GCP, referred to as the IHMCL-GS1 Code, is 8907272. This code serves as the basis of the unique and proper identification of each FASTag within the NETC (National Electronic Toll Collection) system.
Digital Payments: FASTag facilitates digital payments through the RFID tag. The RFID readers installed at the highway toll plazas read EPC and trigger the payment transfer.
Standardised Toll Collection: With FASTag, the whole toll collection process becomes structured and standardised. GS1 standards make this process smoother and efficient. This is necessary to verify that every process in the supply chain works in a structured manner across the whole nation and ultimately globally.
Cashless Payment - FASTag allows customers to travel without stopping at toll plazas. This results in reduced congestion on highways and fosters faster journeys.
RFID tags can promote greater product visibility in the supply chain. This helps manage inventory in real time, avoiding situations of overstocking and stockouts.
RFID technology works by using radio waves to transmit data between a tag and a reader for identification and tracking purposes.
RFID improves productivity by enabling real-time tracking, reducing manual data entry, and streamlining inventory management.
RFID helps retailers improve inventory accuracy, enable track & trace of products, reduce theft, and optimise supply chain efficiency.
RFID does not require direct line-of-sight and can read multiple tags simultaneously. Traditional barcodes require manual scanning and a direct line of sight.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *