2D barcodes are a step beyond the classic barcodes on product packaging. These two-dimensional versions store a significantly larger amount of data. These barcodes are now integral to various industries, offering enhanced functionalities. For instance, in healthcare, 2D barcodes streamline patient record management and drug tracking, which facilitates counterfeit detection. In retail, they improve inventory control and provide a seamless way for consumers to access detailed product information or engage with digital promotions. Overall, the adoption of 2D barcodes has revolutionised operational efficiencies and customer interactions.
Types of 2D Barcodes
Here’s an overview of the different types of 2D barcodes and their distinct characteristics and applications:
QR Codes
Quick Response (QR) codes are among the most recognisable types of 2D barcodes. They can store website URLs, phone numbers, or up to 4,296 alphanumeric characters, facilitating a wide range of applications from advertising to digital payments. QR codes are advantageous due to their ease of use and widespread smartphone support, though they are less secure than some alternatives.

Data Matrix Codes
Often used in electronics and healthcare, Data Matrix codes are highly secure and capable of encoding up to 2,335 alphanumeric characters. Their compact size makes them ideal for small items, and they remain readable even when partially damaged, thanks to reliable and effective error correction.

Choosing the Right 2D Barcode for Your Needs
Choosing the ideal 2D barcode for your business depends on your specific requirements, keeping in mind the standards set by GS1. Key factors include the data capacity needed, the physical size limitations of the items being tagged, and the scanning environment.
QR codes are perfect for engaging consumers as they’re widely recognised and easy to scan with smartphones. Also, consider the barcode’s error correction ability and compatibility with existing scanning technology to ensure seamless integration.
Tips on Implementing 2D Barcodes in Your Business
To integrate 2D barcodes, begin by assessing your data requirements and selecting the appropriate barcode type. Ensure that the design of your barcodes is clear and easily scannable, compatible with your products and the scanners you use. Conduct regular testing to prevent scanning issues in operational environments. This approach will help integrate 2D barcodes smoothly into your business processes, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and data management across various operations.
Benefits of Using 2D Barcodes
2D barcodes bring several advantages that streamline operations and enhance user engagement across various industries. Here’s how they can benefit your business:
- Increased Data Capacity: 2D barcodes can hold a vast array of information in a compact form, from simple URLs to complex serialized data, making them incredibly efficient for storing large amounts of data on small product labels.
- Enhanced Security: With advanced encryption and error correction features, 2D barcodes enhance the security and integrity of the data they contain, reducing the risks of tampering and errors.
- Improved Inventory Management: These barcodes allow for the tracking of products through every stage of the supply chain, providing accurate, real-time inventory data that helps businesses manage stock levels more effectively.
- Better Traceability and Product Authentication: 2D barcodes enable easy verification of the origins and authenticity of products, which is crucial in combating counterfeiting and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Cost-effectiveness: By reducing errors and increasing efficiency in processes like inventory management and checkout procedures, 2D barcodes can significantly lower operational costs.
These benefits make 2D barcodes a valuable tool for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of 2D barcodes and their specific applications can significantly enhance how a business operates and interacts with its customers. Standards-based barcodes can streamline processes, enhance user engagement, and provide secure data management. From enhancing inventory management and ensuring product authenticity to boosting customer engagement through quick and reliable data access, the benefits are extensive. Businesses can leverage 2D barcodes to not only streamline operations but also to safeguard data integrity, thereby achieving a higher level of efficiency and security. The strategic implementation of 2D barcodes is thus a vital step towards modernising business practices and improving overall operational performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which barcode is the best?
The best barcode depends on your specific needs. For instance, QR codes are great for consumer-facing applications due to their smartphone compatibility and Data Matrix codes offer excellent durability and compact size for industrial use. Evaluate your requirements, such as data capacity, security needs, and environmental factors, before choosing.
2. What is a 2D barcode?
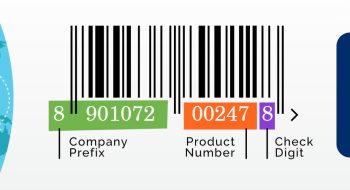
A 2D barcode is a graphical representation that stores more information, unlike 1D barcodes which store less or limited information. 2D barcodes can contain a variety of information including URLs, serial numbers, and much more, allowing for more complex data storage.
3. What is a 2D barcode called?
2D barcodes are referred to by specific names based on their patterns and structures, such as QR codes, or Data Matrix.
4. What is the most common 2D barcode?
The most common 2D barcode is the QR code. It is widely used across various sectors due to its ease of use with smartphones, high data capacity, and quick readability, making it highly popular for both commercial and personal applications.
5. Where are 2D barcodes used?
2D barcodes are used in many sectors including retail, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. They help in tracking products, managing inventory, providing detailed product information to consumers, and ensuring authenticity and traceability of goods.
6. How big is a 2D barcode?
The size of a 2D barcode can vary greatly depending on the size of the packaging and other scanning requirements. They can be small enough to fit on a tiny component or large enough to be scanned from a distance on a shipping container.
7. How to get a 2D barcode?
To make a 2D barcode, you first need to register with GS1 India to obtain GS1 barcode numbers (GTINs/EAN) for your products. The process involves selecting the required number of barcodes, filling out the registration form, uploading necessary documents such as your company’s PAN card, GST/VAT registration certificate, and proof of sales turnover, and then paying the applicable fees. After the registration, you can manage and allocate your barcode numbers using the DataKart service.
8. Can a 2D scanner read a QR code?
Yes, a 2D scanner is designed to read QR codes along with other types of 2D barcodes. These scanners use imaging technology to capture the barcode and decode the information contained within, regardless of the barcode’s orientation.