ITF-14 is a type of one-dimensional barcode used on higher level packaging units such as corrugated boxes to facilitate product identification throughout the supply chain. While you are likely familiar with using EAN (European Article Number), GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) or UPC (Universal Product Code) codes to identify individual products or SKUs (Stock Keeping Units), the ITF-14 is specifically used to track and manage pallets that carry these products in bulk. This blog will be a guide in understanding and exploring the role of this ITF-14 barcode in the logistics industry, in detail. We will also uncover how this barcode type benefits the supply chain and the role of GS1 India in issuing this barcode.
What is an ITF-14 Barcode?
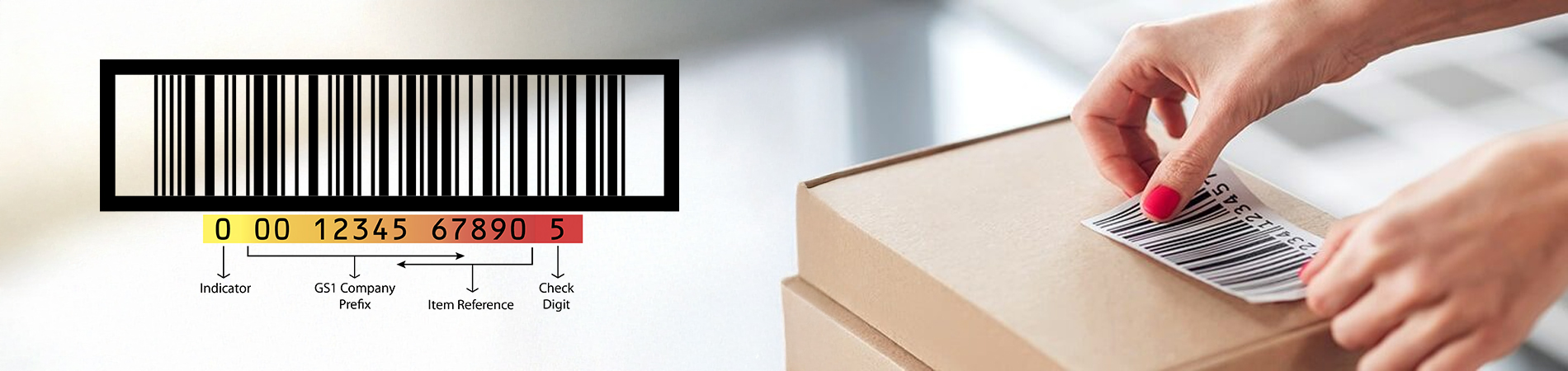
Unlike EAN or GTIN which is used specifically on products sold at point-of-sale, ITF-14 barcodes have a more comprehensive role to play. ITF-14 barcodes encode a 14-digit GTIN. The barcode can either be printed on a label or directly on a corrugate.
An ITF-14 barcode is similar to a GTIN-13 in composition with the only difference being the indicator digit (digits ranging from 0 to 9 to identify different packaging levels within the product hierarchy). The minimum size of an ITF-14 barcode is 1.25 inches tall and is applied in general distribution and logistics and can only carry the GTIN. In case, GTIN-12, GTIN-13 or GTIN-8 are to be used to encode in an ITF-14 barcode, filler zeroes (0) need to be added before GTIN.
ITF-14 Barcode Format
Though ITF-14 is like any other 1D barcode, what separates it from others is its thick black borders, called bearer bars. This bearer bar is a prominent identifying feature of an ITF-14 barcode, and as a matter of fact, no other barcodes have thick black borders. One crucial reason behind the presence of these bars is to improve readability and durability even in challenging conditions. Below listed are a few things that you can consider to quickly identify an ITF-14 barcode –
- Look for the thick borders (bearer bars)
- Check for a 14-digit number encoded within the barcode.
- Verify that the barcode is on the outer packaging.
- The pattern of black and white vertical lines
The presence of bearer bars forms a box-shaped figure outside.
Below provided is a breakdown of GTIN encoded in an ITF-14 barcode –
- Indicator Digit – You can add an indicator digit to create different GTIN-14s for various groupings of the same product, like cartons or pallets. The digit ‘0’ is reserved for a GTIN-14 applied on a pallet containing products of the same variables; weight or volume (homogenous series). Similarly, digit ‘9’ is reserved for GTIN-14 of pallets containing products of different variables; weight or volume (heterogeneous series).
- Country Code – It is the code allotted by GS1 Global to the GS1 member organisation. Every GTIN starts with a country code. GS1 India has ‘890’ as its country code and all unique identification keys in India start with this number alone, representing exclusivity and authorisation.
- Company Code – The company prefix is the unique identification number assigned by the GS1 member organisation to the company registered with it. This company code uniquely identifies the company from others in the market.
- Product Code – Country code and company code together form to construct GCP (Global Company Prefix). This is followed by a product code which depends on the company’s use and coding needs. It uniquely identifies products or SKUs manufactured by the company.
- Check Digit – The final component of a GTIN is a check digit which is a mathematically calculated digit. It is used to validate the GTIN composition and ensure the GTIN is correct by all means. This algorithm of mathematically calculating check digit is also referred to as Luhn Algorithm (also known as Modulo 10).
GS1 plays an indispensable role in standardising the usage and implementation of barcodes in India. In the context of the ITF-14 barcode, GS1 has defined standards for the usage of ITF-14, exclusively limiting its usage in the logistics industry. Various other standards of usage are defined by GS1 for products’ unique identification. ITF-14 is restricted for higher levels of packaging as defined by GS1 standards. The blog will cover the reasons and benefits of doing so.
Benefits of ITF-14 Barcodes
ITF-14 barcode plays a crucial role in streamlining supply chain operations. Below are some benefits that the ITF-14 barcode offers in the industry –
- Improved Supply Chain Visibility: When the ITF-14 barcode is applied on higher level packaging like cartons or pallets, it improves the supply chain visibility of products. Businesses can easily track or trace the shipments if required and different supply chain stakeholders can directly scan cartons/boxes to verify products at each level. This also fosters transparency and strengthens trust between different supply chain levels.
- Easy Handling of Bulk Shipment: By enabling rapid, unique identification of bulk shipments, ITF-14 barcodes ensure products are easily handled, monitored and supplied throughout the supply chain. Their use also minimises human errors and speeds up the entire process, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Global Compliance with Trade: The ITF-14 barcode is compatible with international trade as it meets global trade requirements and conforms to regulations.
- Streamlined Inventory Management: With ITF-14 barcodes, businesses are able to carry out accurate inventory management. They facilitate easy tracking of products and help businesses avoid situations of overstocking and stockouts.
How to Create an ITF-14 Barcode?
In case businesses want to use ITF-14 barcodes to comply with trade regulations and meet their packaging needs, they will first need to get registered with GS1 India for barcodes. Once your registration is complete (How to get registered for GS1 Barcodes?), you can follow the steps listed below to create an ITF-14 barcode –
Step 1: Add an indicator digit, from 1-8, on a case of individual items.
Step 2: If you want to uniquely identify a pallet of cases comprising individual items, you would have to add indicator digit 2. The series can go for as long as you do not reach 8.
Step 3: Once you have utilised all digits from 1-8, you will have to switch to a new GTIN.
Step 4: As a last step, you can test and verify the ITF-14 barcode to avoid unnecessary trade complications.
Conclusion
ITF-14 barcodes can effectively scale up your operations allowing you the opportunity to supply a variety of products at the same time and at the same location. In India, its use is very limited with the transport industry gradually shifting to 2D barcodes or SSCC (Serial Shipping Container Code) with their ability to encode more information. With these barcodes’ wide acceptance and usability across the world, they simplify processes and make it easier for people involved in the process to interpret the information coded. With benefits ranging from effective inventory management, track and trace of products, and also better visibility in the operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is ITF in a barcode?
ITF-14 is a type of one-dimensional barcode which encodes GTIN-14. It is used to identify packaging at higher levels, mostly pallets and corrugated boxes containing multiple products.
2. What is the ITF-14 barcode used for?
ITF-14 barcodes are used to identify higher-level packaging materials throughout the supply chain.
3. How to convert EAN-13 to ITF-14?
To convert EAN-13 into an ITF-14 or GTIN-13 to GTIN-14 you simply would need to add one zero preceding the GTIN number.
4. What is the difference between ITF-14 and 128?
One distinguishing difference between the ITF-14 and GS1-128 barcodes is the presence of thick black borders (the bearer bars) outside the ITF-14 barcode. These bearer bars are not present in the GS1-128 barcode.
5. What does ITF stand for barcode?
ITF stands for Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) which encodes only numeric digits in pairs and has only even numbers. ITF barcode is interleaved which means it encodes two digits simultaneously, reducing the length of the bar.