In the modern world, traceability has become a cornerstone for ensuring transparency, safety, and efficiency in various industries ranging from food to healthcare and manufacturing to logistics. At its core, traceability allows the tracking of products from their origin through every stage of their journey, ensuring quality control, authenticity, and compliance with regulations. This blog delves into how the evolution of barcodes has been essential in enhancing tech-enabled traceability systems.
Definition of Traceability
Traceability refers to the capability to trace the history, journey, or location of an entity by recorded identifications. In various industries, traceability is crucial for verifying the authenticity of products, managing recalls efficiently, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and enhancing customer trust. Traditional barcodes, consisting of a series of vertical bars of varying widths, have long been the backbone of traceability systems. However, their limited data capacity and susceptibility to damage have necessitated the development of more robust solutions.
Evolution of Barcodes
The journey from traditional barcodes to more sophisticated forms marks a significant evolution in traceability technology. Traditional barcodes have been instrumental in streamlining operations but faced limitations in data storage.
The Shift to 2D Barcodes
2D barcodes, such as QR codes and Data Matrix, have revolutionized traceability with their ability to store vast amounts of data, including manufacturer details, serial numbers, and even web links, in a compact format. These barcodes can be scanned from any direction, improving efficiency and reducing errors in the scanning process.
RFID Technology and Its Impact
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. RFID tags can store a wide range of information and do not require a line of sight for scanning, significantly enhancing traceability across supply chains.
Introduction of Data-Rich Barcodes
Data-rich barcodes like GS1 DataBar (DataBar was used for smaller items with less space for a barcode) and PDF417 (PDF417 is not related to GS1 India) have further expanded the capabilities for detailed traceability. These barcodes can hold extensive information, including batch numbers and expiry dates, facilitating more precise tracking and management of products.
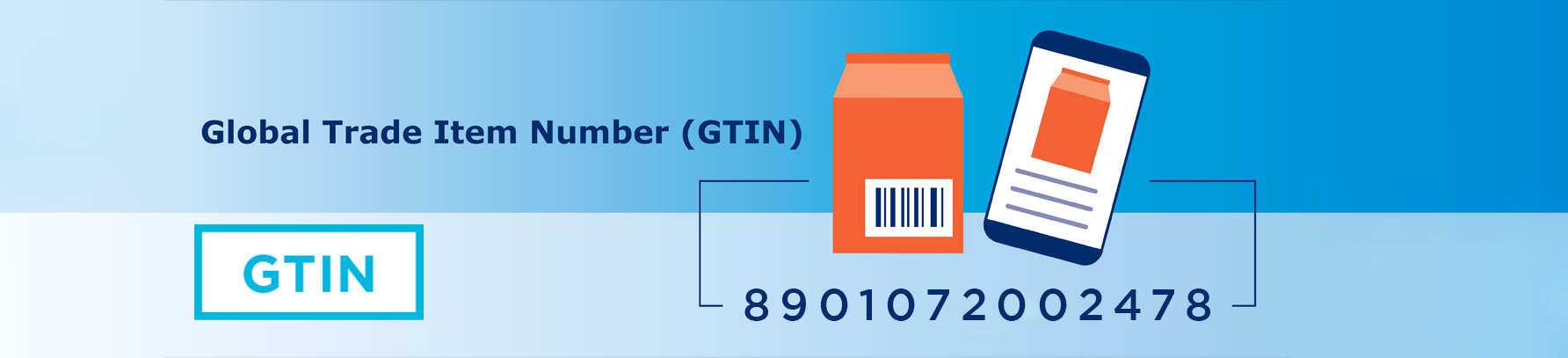
GS1 Digital Link
GS1 Digital Link revolutionises product identification by transforming traditional barcodes into gateways for online content. By scanning a single barcode, consumers and businesses can access extensive information such as product origins, authentication, user manuals, and more, significantly improving transparency and traceability across supply chains.
Revolutionising Traceability with GS1 Digital Link
GS1 Digital Link extends the functionality of barcodes by linking them to digital content on the web. This innovation offers immense benefits for traceability, including dynamic data access, enhanced consumer engagement, and the ability to update information in real time, which is particularly useful for managing product recalls and ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Tech-Enabled Solutions for Traceability
The integration of barcodes with advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Data Matrix codes has opened up new avenues for creating more resilient and efficient traceability systems.
Integration with IoT
IoT technology enables real-time tracking and monitoring of products through sensors and smart devices, providing unprecedented visibility across the supply chain. When combined with barcode technology, IoT enhances traceability by automating data collection and providing detailed insights into the condition and location of products.
Integration of Data Matrix Codes in Traceability Systems
Data Matrix codes are increasingly being incorporated into traceability systems for their high data density and error correction capabilities. These codes are instrumental in tracking and tracing products, especially in industries where space on the product is limited.
Real-world Applications of Tech-enabled Traceability
The advent of tech-enabled traceability systems has modernised several industries by enabling the precise tracking and verification of products throughout their lifecycle. In the food industry, these systems ensure the safety and authenticity of food products by tracking their journey from farm to table. This not only helps in quickly identifying and addressing potential contamination issues but also enhances consumer confidence in the safety and quality of food products.
In healthcare, traceability technologies play a critical role in managing pharmaceuticals and medical devices. By meticulously tracking the distribution and usage of these products, healthcare providers can significantly improve patient safety. This technology aids in the prevention of counterfeit medicines entering the supply chain and ensures that medical devices are used within their validity periods, thereby reducing the risk of adverse health outcomes.
Within the manufacturing and logistics sectors, traceability systems are important in optimising production and distribution processes. They offer real-time visibility into the supply chain, allowing companies to monitor the movement of goods, manage inventory more effectively, and reduce the likelihood of errors. This heightened efficiency and reliability not only reduce operational costs but also improve customer satisfaction by ensuring the timely delivery of products.
Overall, tech-enabled traceability is a key driver of transparency, efficiency, and quality across various industries, underscoring its importance in the modern economy.
The Future of Traceability and Barcodes
The future of traceability and barcodes is set to be transformed by emerging technologies, marking significant advancements in how we track and authenticate products across various industries. Innovations in barcode technology, such as the development of more sophisticated, high-capacity QR codes and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags, are at the forefront of this evolution. These technologies promise enhanced data storage capabilities, enabling the embedding of extensive product information, from origin to expiration dates, directly within the code.
Additionally, blockchain technology is poised to upgrade traceability systems by offering unparalleled transparency and security in supply chains. It allows for the creation of immutable records of product journeys, ensuring authenticity and compliance with regulatory standards. Predictions for the evolution of traceability systems also include the integration of AI and machine learning, which could automate and refine the process of tracking, detecting counterfeit products, and predicting supply chain disruptions. Together, these advancements suggest a future where traceability systems are more efficient, secure, and transparent, benefiting businesses and consumers alike.
Conclusion
The evolution of barcodes from simple linear identifiers to complex, data-rich symbols has been instrumental in driving advancements in traceability. As technology continues to advance, the integration of barcodes with digital solutions like GS1 Digital Link, IoT, and emerging technologies will further revolutionise traceability, ensuring greater transparency, efficiency, and safety across all industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do data matrix codes differ from traditional barcodes?
Data Matrix codes differ from traditional barcodes in several ways. Unlike linear barcodes that store data in a series of parallel lines, Data Matrix codes are 2D and encode information in a grid of black and white cells. This allows them to hold much more data in a smaller space, including alphanumeric characters and binary data, making them more versatile and efficient for various applications.
2. What are the benefits of using data matrix codes for traceability?
The benefits of using Data Matrix codes for traceability include their high data capacity, ability to encode information directly on items with very small print areas, and resilience to damage. They can store significant amounts of data, such as serial numbers, lot codes, and expiration dates, directly on the product, enhancing traceability throughout the supply chain. Their error correction capabilities ensure data can be retrieved even if the code is partially damaged.
3. How does GS1 Digital Link enhance barcode technology?
GS1 Digital Link enhances barcode technology by transforming traditional barcodes into gateways for accessing a wide range of information online. It leverages web URLs encoded within barcodes, allowing consumers and businesses to access product information, user manuals, and traceability data by scanning a QR code or Data Matrix. This connectivity offers a seamless bridge between physical products and digital data.
4. How does barcode scanning technology contribute to traceability systems?
Barcode scanning technology plays a crucial role in traceability systems by enabling the quick and accurate capture of product information at various points in the supply chain. It facilitates inventory management, tracks the movement of goods, and helps verify the authenticity of products, contributing significantly to the efficiency and reliability of traceability systems.
5. Can existing barcode systems be easily integrated with GS1 Digital Link?
Existing barcode systems can be integrated with GS1 Digital Link, allowing businesses to utilize their current infrastructure while adopting new capabilities. This integration is facilitated by the use of standardized identifiers and the flexible nature of GS1 Digital Link, which can encode existing data formats within a QR code or Data Matrix, enhancing the utility of existing barcodes.
6. What are the primary challenges in implementing tech-enabled traceability systems?
The primary challenges in implementing tech-enabled traceability systems include the need for a significant initial investment in technology and training, the complexity of integrating new systems with existing operations, data privacy and security concerns, and ensuring interoperability across different systems and standards. These challenges require careful planning, investment, and collaboration among stakeholders to successfully implement and benefit from advanced traceability systems.