Overview
Organisations are required to carry out due diligence to avoid any such occurrences that may cost them resources such as money, time, and labour. However, there are some scenarios where companies are unable to ensure this due diligence requires the need for product recalls. In simple terms, recall is the activity of calling back the products supplied in the market upon realising the defects to ensure consumer safety.

What is a product recall?
A product recall is the activity of initiating retrieval of products that may either be defective, expired, or infected, from the market to avoid jeopardization of consumer safety and business performance. The recall request is raised by the supplier/business owner upon identifying the defects. Not recalling faulty products from the system can call serious regulatory actions making it essential to identify and take necessary actions at the earliest.
How to manage a product recall procedure
The successful implementation of the whole recall procedure is highly crucial. Handling and managing the recall process is a very delicate process and needs a perfect equilibrium of support from all parties involved and alertness. Here’s a quick guide for you to successfully manage a product recall procedure.
1. React quickly
The reaction is critical in the event of default, no reaction can result in the consumption of faulty products which can sabotage the health, happiness, or experience of the consumers.
2. Notify authorities
Once you have identified the issue it is crucial to inform the authorities or agencies involved as quickly as possible. There may or may not be specific recall guidelines that you may have to follow depending on the product you serve and in which industry.
3. Give an explanation
To leave a positive impact, it is important to explain your product recalls to the end consumer. It helps maintain goodwill and ensures consumers understand the reason behind your sudden course of action.
4. Be available for questions
To avoid chaos, it is always advised to address public concerns, questions, or outrage if any. To make things easier you can set up an email account or provide a phone number for consumers to shoot their grievances.
5. Offer refunds
Business owners will have to provide full refunds or provide a functional/ fit-to-consume product to consumers. It serves as an opportunity to preserve customer relationships.
6. Use product recall insurance
Product recall is a costly process and can drain organisations of their hard-earned money. It is therefore radical to use insurance in such cases to cover costs such as shipping, disposal, and advertising.
7. Reintroduce the product
After the product is recalled from the market, start planning on the reintroduction of the product. The procedure can include strategizing marketing plans and agendas and taking consultations to avoid such instances in the future.
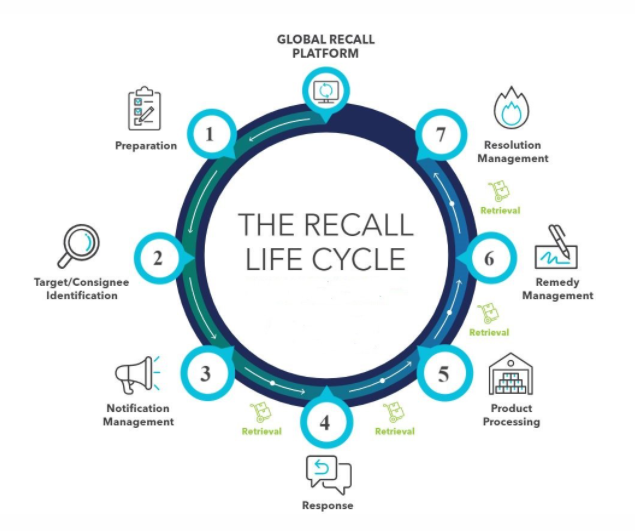
Types of Product Recall
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies product recalls into three classes, with Class I being the products with the highest chances of posing injuries or even death. Products that can cause injuries or temporary illness fall in Class II, and products that are not harmful but still violate the regulations fall in Class III.
Class I: Recalls
The safety of the consumers is supreme and hence products that pose the greatest threat to this safety fall under Class I recalls.
Class II: Recalls
Class II recalls happen when there are remote chances of causing adverse health conditions or the product is capable of inflicting medically reversible consequences.
Class III: Recalls
When the risk involved is near to nil, such products fall in the Class III category. Consumer exposure to such products will unlikely result in adverse health conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What types of products are typically recalled?
Food and drug-related, vehicles, or any other products that have the power to negatively impact consumers are typically recalled from the market.
2. How are product recalls announced to the public?
The organisation is liable to promptly inform the consumers through print, paper, or electronic media. It must also apprise the local/concerned authorities as a precautionary measure. The announcement should contain details such as the name of the organisation recalling the product and the product name, the date of manufacturing, the actions that the consumer should take, and a “do not consume” message. It must also have an emergency contact number.
3. Who is responsible for enforcing product recalls?
As per the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution for product recalls, manufacturers or retailers are compelled to recall any product from the market that is deemed unfit for consumers. The guidelines provide the framework in which manufacturers or retailers have to operate, starting from informing government entities to informing the end consumers.
4. Are all recalled products completely removed from the market?
Yes, all the recalled products are completely removed from the market and consumers are compensated with either a full refund of the product or by providing a replacement of the product.
5. Can a product be recalled more than once?
A product can be recalled more than once if more than one contamination is identified. It can also be recalled more than one time when more lot number variations or retail locations are identified.
6. What steps should companies take to prevent future recalls?
Thoroughly know your product before releasing it in the market. Make sure the product is compliant with the industry regulations. Do product testing before the launch to identify any gaps, and make sure the product is 100% safe. Additionally, product inspections throughout the supply chain can help businesses resolve any catastrophe at the earliest.
7. Are there any penalties for companies that fail to initiate a recall?
As per the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, any company or entity that fails to recall products from the market as and when asked by the concerned authority is liable to face criminal actions and civil liability.