Barcodes have become an indispensable tool in the food industry, streamlining operations from farm to table. This blog explores the critical role of barcodes in Food and Retail and how it improves efficiency, ensuring product traceability, and complying with regulatory standards. With this article, gain insights into the different types of barcodes used in food products, the benefits they offer, and best practices for implementing them effectively.
The Basics of Barcodes in Food Products
Barcodes have revolutionized the way industry experts manage and process food products, offering a seamless bridge between physical goods and digital information.
What Are Barcodes in Food Products?
Barcodes in food products are unique, machine-readable codes consisting of a series of black bars and white spaces. They serve a critical role in the food industry by enabling efficient identification, tracking, and management of products. These barcodes store essential data like product type, origin, and price, which can be easily scanned and processed. Commonly used types include the Universal Product Code (UPC), which is prevalent in retail, and the GS1 Data Bar, favored for its compact size and capacity to encode additional information such as batch numbers and expiration dates. These diverse barcode formats cater to various packaging needs and information requirements in the food industry.
Benefits of Using Barcodes in the Food Industry
Barcodes significantly enhance efficiency in managing food products. Their application streamlines the process of tracking items throughout the supply chain, from production to point of sale. This efficiency is especially evident in inventory management, where barcodes allow for real-time tracking of stock levels, reducing the likelihood of overstocking or stockouts. Additionally, barcodes facilitate quick and accurate data entry, minimizing human errors commonly associated with manual processes. This level of accuracy and efficiency is vital in the food industry, where managing perishable items and ensuring their freshness is paramount. Moreover, barcodes aid in efficient recall procedures if needed, thereby ensuring consumer safety and maintaining trust.
Barcode used in Food Products – EAN, Universal Product Code (UPC)
The Universal Product Code (UPC) is a widely recognized barcode system that is predominantly used in the food industry to identify products. Each UPC barcode consists of a 12-digit numerical code, uniquely representing an item, making it easier for retailers to track and manage inventory. The structure of a UPC barcode includes a leading digit that often indicates a product’s category, followed by a manufacturer code and a product code, and finally, a check digit to ensure accuracy. This standard format allows for quick scanning at points of sale and efficient inventory management. UPC barcodes are fundamental in retail environments, streamlining the checkout process and aiding in logistics and stock control.
Implementing Barcodes in Food Products
The integration of barcodes into food products requires strategic planning and the right tools to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
How to Create Barcodes for Food Products
Creating barcodes for food products involves a few key steps. First, determine the type of barcode needed, such as UPC or GS1 DataBar, based on the product and its packaging. Next, obtain a unique product identifier from GS1, which ensures global uniqueness. Once you have the identifier, use barcode generation software to create the barcode image. Software options range from basic online generators to advanced tools offering customisation and batch processing. These tools convert the identifier into a scannable barcode format, suitable for printing and labelling on food packaging. Finally, integrate the barcode into the product’s packaging design, ensuring it’s clearly printed and easily scannable.
Barcode Printing and Labelling
Barcode printing and labelling are crucial in the food industry for ensuring the effective use of barcodes. Proper printing and labelling ensure that barcodes are easily scannable and readable throughout the product’s lifecycle. To ensure barcode quality and durability on food packaging, it is important to use high-quality printers and labels that resist fading, smudging, and damage from environmental factors like moisture and temperature changes. The barcode should be printed in a high-contrast colour scheme, typically black on white, to enhance readability. Additionally, placing the barcode on a flat, easily accessible area of the packaging without folds or curves will ensure consistent scanning. Regular quality checks are essential to maintain the integrity of the barcodes throughout the product’s distribution and retail lifecycle.
Using Barcodes for Traceability and Compliance
In the world of food safety and supply chain management, barcodes have emerged as a vital tool, enhancing traceability and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Food Safety and Traceability
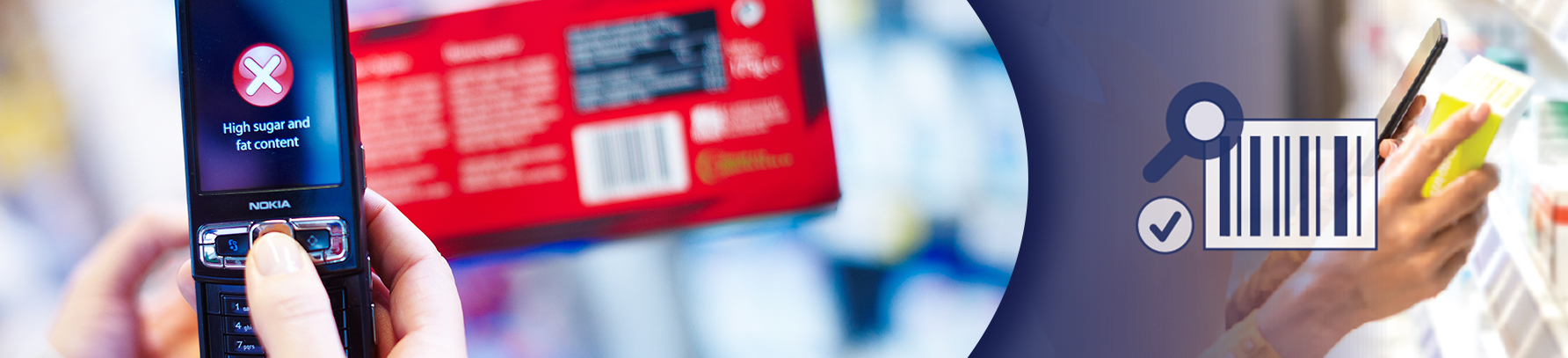
Barcodes play a pivotal role in food safety and traceability, acting as digital fingerprints for food products. They enable quick and precise tracking of items from production to the point of sale, which is crucial in managing the food supply chain. This capability is essential not only for operational efficiency but also for public health. In the event of a food safety concern, such as contamination, barcodes allow for rapid identification and recall of affected products, minimizing health risks to consumers.
Regulatory bodies across the globe mandate the use of barcodes in the food industry to uphold these safety standards. For instance, laws often require detailed labelling, including batch numbers and expiration dates, to ensure that consumers receive crucial product information. Barcodes simplify compliance with these regulations by embedding necessary data in a compact, machine-readable format.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations
Numerous food companies have harnessed the power of barcodes to enhance their operations. Indian army has implemented food traceability all across India for tracking both dry and wet ration. This initiative not only streamlined their inventory management but also significantly reduced instances of food wastage. A notable example is Reliance Retail – a large supermarket chain that implemented a barcode system for product listing and catalogue management.
These case studies underscore the transformative impact of barcodes in the food industry. By adopting this technology, companies have not only adhered to regulatory requirements but also gleaned valuable insights into their supply chains, leading to improved business practices and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Barcodes are a fundamental technology in the food industry that ensure safety and compliance. Their ability to streamline processes, ensure traceability, and meet regulatory standards underscores their indispensable role. Embracing barcodes in food products and packaging is not just a trend but a vital strategy for efficiency and consumer trust in today’s fast-paced market.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of barcodes in food products?
Barcodes serve as an efficient tool for managing inventory, ensuring product traceability, and enhancing transaction accuracy.
2. How do barcodes improve efficiency in the food industry?
Barcodes streamline inventory management, reduce errors, and accelerate checkout processes.
3. What are the different types of barcodes commonly used in food products?
Common types include UPC and GS1 DataBar, each serving different packaging and information needs.
4. How do I create barcodes for my food products?
Barcodes can be created using specialized software and tools that generate and assign unique identifiers after registering with GS1 India.
5. What are the regulatory requirements for using barcodes in the food industry?
Regulations focus on ensuring accurate labelling and traceability, often requiring specific barcode types for different products.
6. Can you explain the significance of GS1 DataBar in the food industry?
GS1 DataBar is significant for its ability to encode more data in a smaller space, ideal for small or perishable items.
7. What are the best practices for printing and labelling barcodes on food packaging?
Best practices include ensuring clear, durable printing and appropriate placement on the packaging.
8. How do barcodes enhance food safety and traceability?
Barcodes enable quick tracking of products, aiding in efficient recalls and adherence to safety standards.
9. Are there any software or tools recommended for barcode creation in the food industry?
GS1 India is the exclusive authority for distributing unique and internationally accepted barcodes in India. For barcode creation in the food industry, GS1 India offers specialized tools and software like DataKart.
10. Can you provide examples of food companies successfully implementing barcodes for traceability and compliance?
AOV group, Ideal AgriSearch are successfully using barcodes, enhancing their supply chain management and regulatory compliance.