Introduction
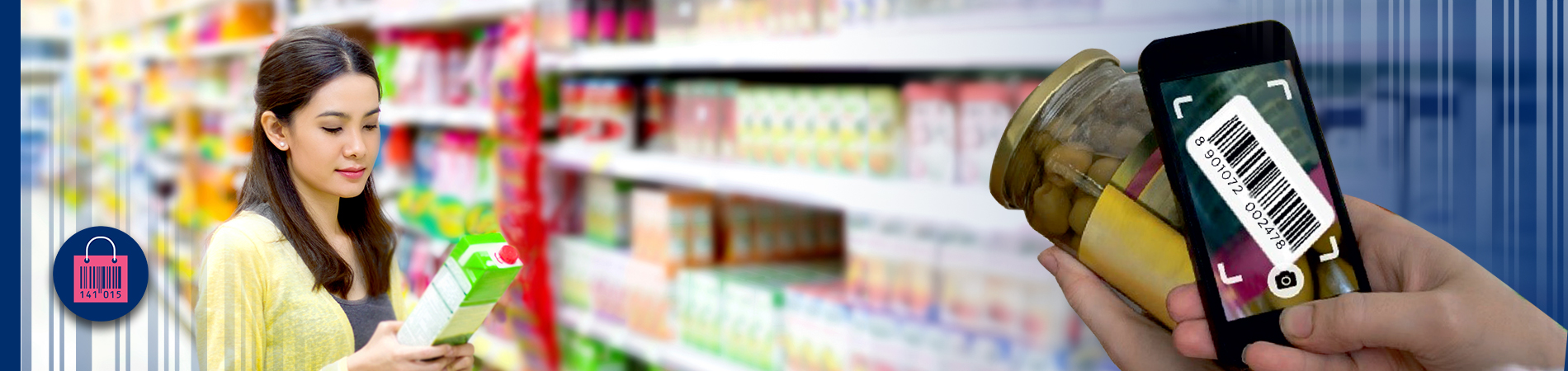
The European Article Number (EAN) is a globally recognised standard for product identification in trade and retail. EAN numbers uniquely identify products, facilitating seamless tracking from manufacturing to retail. By scanning EAN numbers, businesses can verify product authenticity, ensuring consumers receive genuine items. This process helps prevent counterfeits and enhances supply chain transparency, leading to a more efficient and trustworthy shopping experience. This blog explores how scanning EAN numbers boosts consumer trust by ensuring product authenticity, reducing counterfeit risks, and improving the overall shopping experience through enhanced transparency and verification.
What is an EAN Number?
Definition and Purpose
An EAN is a unique identifier used to distinguish products worldwide, facilitating seamless trade and inventory management across various industries. It helps in the accurate tracking of products from manufacturing to retail, ensuring that each product is easily identifiable and traceable.
Structure of an EAN
An EAN typically consists of 13 digits, each segment providing specific information such as the country of origin, manufacturer, and product type. This structured format ensures precise identification and tracking of products, making it easier for businesses and consumers to verify product authenticity.
The Importance of EAN Number Check
Ensuring Product Authenticity
Verifying an EAN number confirms the legitimacy of a product, ensuring it is not counterfeit and meets the specified standards of the manufacturer and regulatory bodies. This verification is crucial for maintaining trust in the marketplace and ensuring that consumers receive genuine products.
Preventing Counterfeits
The widespread use of EAN helps reduce the circulation of counterfeit goods. By checking EAN numbers, retailers and consumers can identify and avoid fake products, maintaining market integrity. This practice is essential for protecting both the brand and the consumer from the adverse effects of counterfeit products.
Enhancing Supply Chain Transparency
EAN checks facilitate tracking products from the manufacturer to the end-consumer, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. This visibility helps in managing recalls, quality control, and efficient inventory management, thereby reducing risks and improving operational efficiency.
How Scanning EAN Builds Consumer Trust
Instant Product Verification
At the point of sale, scanning an EAN allows for real-time validation of a product. This instant verification reassures consumers that they are purchasing genuine products. The ability to quickly and accurately verify product authenticity at the checkout point enhances the shopping experience and builds trust.
Detailed Product Information
Scanning an EAN provides access to comprehensive product details, including ingredients, manufacturing date, and compliance with safety standards. This information empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they know exactly what they are buying.
Reduction of Purchase Anxiety
Knowing a product is genuine alleviates consumer concerns, reducing purchase anxiety. EAN verification builds confidence, encouraging consumers to trust the products they buy. This trust is fundamental to fostering long-term customer relationships and repeat business.
Boosting Consumer Confidence with EAN Scans
Improving Shopping Experience
Seamless EAN scanning enhances the overall shopping experience by ensuring quick and accurate product identification, reducing checkout time, and minimising errors. This efficiency leads to higher customer satisfaction and a smoother shopping process.
Facilitating Informed Decisions
Providing reliable data through EAN scans enables consumers to make better choices. Information such as product origin, nutritional facts, and user reviews helps in making well-informed decisions. This transparency is key to building consumer confidence and loyalty.
Building Brand Loyalty
Trust in product authenticity leads to repeat purchases and brand advocacy. Brands that consistently deliver genuine products through EAN verification can build long-term loyalty and positive consumer relationships. This loyalty is crucial for sustaining business growth and competitive advantage.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of EAN Scanning
Retail Giants Utilising EAN
Major retailers like Walmart have integrated EAN scanning to enhance customer assurance. These companies use EAN for efficient inventory management and to ensure the authenticity of products on their shelves. The success of these implementations demonstrates the effectiveness of EAN in building consumer trust and operational efficiency.
Positive Consumer Feedback
Consumers have expressed high levels of satisfaction with EAN-verified products. Testimonials and reviews often highlight the confidence that comes with knowing a product is genuine and verified. This positive feedback shows the importance of EAN in enhancing the shopping experience and ensuring product quality.
Integrating EAN Scanning into Your Business
Choosing the Right Scanning Technology
Selecting appropriate scanners and software is crucial for effective EAN number checks. Businesses should have reliable technology that supports quick and accurate EAN scanning. This investment ensures that the verification process is seamless and efficient, enhancing operational efficiency.
Training Staff on EAN Verification
Educating employees on the benefits and procedures of EAN verification is essential. Well-trained staff can efficiently manage EAN scanning, ensuring smooth operations and enhanced customer service. Training programs should emphasise the importance of accuracy and speed in the verification process.
Promoting EAN Verification to Consumers
Marketing strategies should inform consumers about the availability and benefits of EAN checks. Highlighting the role of EAN in ensuring product authenticity can attract more customers and build trust in your brand. Effective communication about EAN verification can differentiate your brand in a competitive market.
Conclusion
EAN scanning significantly boosts trust and consumer confidence by ensuring product authenticity, preventing counterfeits, and enhancing supply chain transparency. This verification process maintains market integrity and fosters positive consumer relationships, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. As technology evolves, EAN verification’s role in building consumer trust and ensuring product quality will become even more critical. The continuous advancement of EAN technology will further strengthen its importance in the marketplace, solidifying its role in fostering trust and confidence among consumers.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How to create an EAN?
To create an EAN, register with a GS1 member organisation to obtain a unique company prefix. Use this prefix along with the product code and check digit to generate the EAN. This process ensures that each EAN is unique and traceable.
2. How to find an EAN number?
An EAN number is usually found below the barcode on the product packaging. Retailers can also use inventory systems to locate the EAN number. Consumers can often find EAN numbers on product labels or by scanning the barcode with a mobile app.
3. What is EAN used for?
EAN is used for identifying products uniquely across the globe, facilitating efficient trade, inventory management, and sales tracking in retail and supply chain operations. It ensures that each product can be accurately tracked from production to sale.
4. What is the formula of EAN?
The EAN formula involves a 13-digit number comprising a country code, manufacturer code, product code, and a check digit, which ensures the EAN’s validity through a specific calculation method. This structure allows for precise product identification and verification.
5. How do you verify an EAN number?
You can verify an EAN number using online databases, mobile applications, or by scanning the barcode at the point of sale to ensure the product information matches the database records. Verification helps confirm the product’s authenticity and traceability.
6. How do I get an EAN code?
To get an EAN code, register with GS1, which will provide a unique company prefix. Combine this prefix with the product identifier and a check digit to create the EAN code. This process ensures that the EAN is unique and compliant with global standards.
7. Is EAN a 13-digit number?
Yes, an EAN is typically a 13-digit number, though there is also an 8-digit version for smaller packages. The 13-digit EAN is more commonly used and recognised globally, providing a robust system for product identification and tracking.