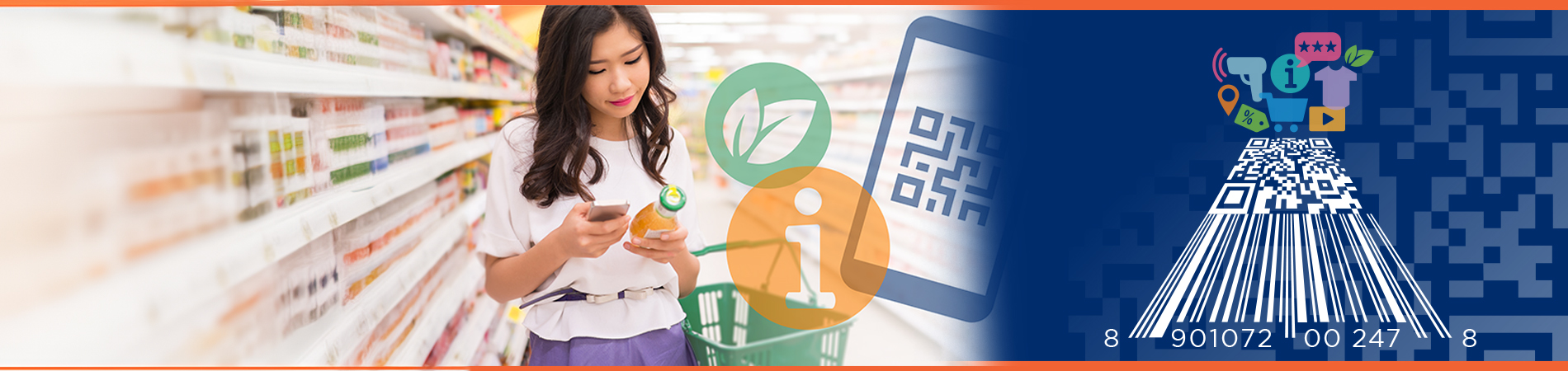
When talking about today’s business environment, efficiency is key. 2D barcodes have emerged as a crucial tool in this regard. Unlike traditional barcodes, which hold limited information, 2D barcodes can store a significantly larger amount of data. This increased capacity enables businesses to track assets and inventory with greater precision, thereby reducing errors such as stock discrepancies, mislabeling, and inefficient data retrieval. These compact yet powerful symbols have changed the way businesses manage their operations, offering enhanced data capacity and a myriad of other benefits compared to traditional linear types of barcodes.
What are 2D Barcodes?
2D barcodes, also known as two-dimensional barcodes, are graphical representations of data that can store significantly more information than their 1D counterparts. Unlike the linear structure of 1D barcodes, 2D barcodes consist of patterns of squares, dots, and other geometric shapes arranged in a grid. This structural difference allows these barcodes to encode a wide range of data types, including text, numbers, and even binary data, making them incredibly versatile.
Why Choose 2D Barcodes for Your Business?
Businesses are increasingly opting for 2D barcodes due to their capacity to simplify operations and elevate data management standards. Recent statistics underscore this trend, revealing a significant uptick in their adoption across diverse industries. From inventory tracking to ensuring product authenticity and fostering interactive customer experiences, they are becoming indispensable assets for forward-thinking businesses. Their versatility and seamless integration with digital systems position them as essential tools for staying competitive. As companies recognise the advantages of using these advanced barcode technologies, they are acknowledging these barcodes to be essential components of their operational strategies, driving efficiency and enhancing overall productivity.
Enhanced Data Capacity and Versatility
One of the primary advantages of 2D barcodes is their ability to store significantly more data compared to traditional 1D barcodes. This capability is crucial for businesses that need to embed detailed product information, track inventory in real time, and manage supply chains efficiently. The inclusion of URLs in 2D barcodes further enhances their versatility, enabling direct access to product details, user manuals, or promotional content, which is particularly beneficial in sectors like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. This feature streamlines operations and boosts accuracy, significantly impacting overall productivity.
Better Customer Engagement and Experience
In addition to their data storage capabilities, 2D barcodes offer businesses the opportunity to enhance customer engagement and provide a superior shopping experience. By embedding additional information or interactive features within the barcode, businesses can offer consumers valuable insights, product tutorials, or exclusive promotions. This enriches the customer experience, strengthens brand loyalty, and fosters a sense of connection between businesses and their customers.
Benefits of Using 2D Barcodes
Utilising advanced technologies like 2D barcodes aligned with GS1 standards can provide significant advantages across various industries, such as:
Efficiency in Scanning
2D barcodes can be scanned from any direction, which speeds up the scanning process. They can also be scanned using mobile devices equipped with cameras, such as smartphones and tablets, allowing for mobile accessibility and convenience.
Enhanced Security
The advanced security features of 2D barcodes, including encryption and data redundancy, provide protection against counterfeiting and fraud. By incorporating these security measures, businesses can protect their products and intellectual property, ensuring consumer trust and brand integrity.
Improved Inventory Management
A core strength of 2D barcodes is streamlining inventory tracking and management processes. Businesses can achieve real-time updates on stock levels and minimize errors, leading to more efficient operations and enhanced customer satisfaction. Whether in retail or logistics, the accuracy and efficiency offered by these barcodes are invaluable.
Better Traceability and Product Authentication
2D barcodes facilitate precise product tracking throughout the supply chain, ensuring traceability and authenticity. This capability is crucial for maintaining product quality and safety standards, ultimately fostering consumer confidence and loyalty.
In conclusion, the advantages of implementing two-dimensional barcodes in your business are undeniable. From increased data capacity to enhanced security and improved customer engagement, they offer a multitude of benefits that can significantly impact business operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a 2D barcode?
A 2D barcode, also known as a two-dimensional barcode, is a graphical representation of data that can store information both horizontally and vertically. Unlike traditional 1D barcodes, which consist of lines and spaces, they contain patterns, dots, or squares arranged in a grid-like format to encode data.
2. Where are 2D barcodes used?
2D barcodes find applications across various industries and sectors. They are commonly used in retail for product tracking and inventory management, in healthcare for patient records and medication tracking, in logistics for shipment tracking, and in marketing for advertising campaigns and interactive experiences.
3. What size is a 2D barcode?
The size of a 2D barcode can vary depending on the specific format and the amount of data it needs to encode. Generally, it can range from small, thumbnail-sized symbols suitable for packaging labels to larger, more complex patterns used for storing extensive data.
4. How do you make a 2D barcode?
To make a 2D barcode, you first need to register with GS1 India to obtain GS1 barcode numbers (GTINs/EAN) for your products. The process involves selecting the required number of barcodes, filling out the registration form, uploading necessary documents such as your company’s PAN card, GST/VAT registration certificate, and proof of sales turnover, and then paying the applicable fees. After the registration, you can manage and allocate your barcode numbers using the DataKart service.
5. Can 2D barcodes be read with a smartphone?
Yes, 2D barcodes can be read with smartphones equipped with barcode scanning apps or built-in camera functionality. These apps use the device’s camera to capture the barcode image, decode the information encoded within it, and display the corresponding data or perform the associated action, such as opening a website link or adding a contact.
6. Why are 2D barcodes considered superior to traditional barcodes?
2D barcodes are considered superior to traditional linear barcodes due to their enhanced data storage capacity and versatility. Unlike 1D barcodes, which can only encode a limited amount of data in a linear format, they can store significantly more information in a two-dimensional grid pattern, accommodating diverse data types and enabling more advanced applications.
7. How do 2D barcodes enhance product traceability?
They will enhance product traceability by enabling precise tracking of items throughout the supply chain. Each barcode contains unique identifiers that can be linked to specific products, batches, or shipments, allowing businesses to monitor their movement from production facilities to distribution centres to retail stores, enhancing visibility and accountability.
8. What types of information can be encoded in 2D barcodes?
2D barcodes can encode various types of information, including alphanumeric characters, numeric data, symbols, and binary data. This versatility allows them to store diverse data sets such as product identification numbers, serial numbers, URLs, contact information, or even entire paragraphs of text, depending on the specific application requirements.