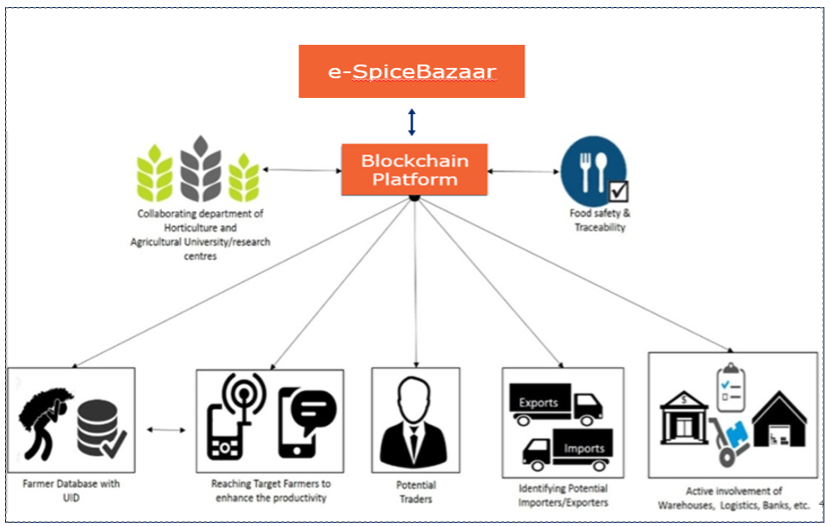
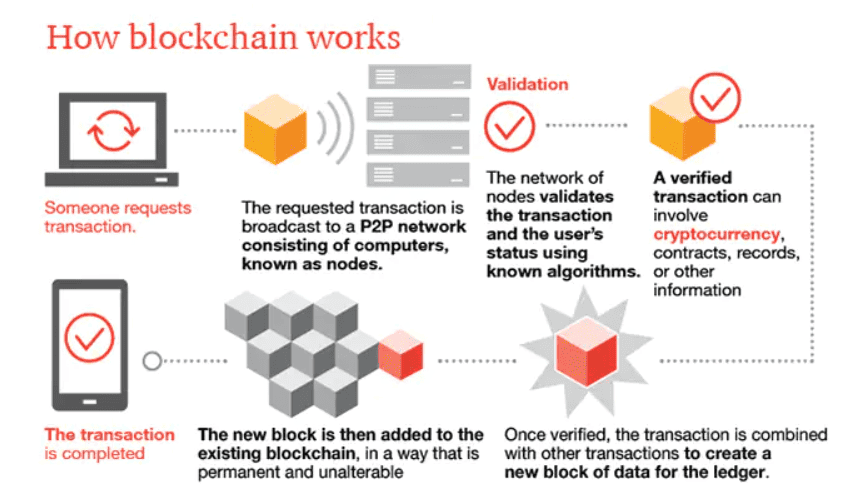
The human body requires food to gain energy for survival and sustenance. Consumed food is broken down inside the body to provide nutrients and release energy. A consistent, balanced, and healthy diet helps regulate energy levels and keeps us active throughout the day. However, with rising concerns over food adulteration and unethical trading practices, food quality is often compromised. In this article, we will explore the challenges faced by the food industry and possible solutions. Readers will learn the importance of GS1 barcodes in maintaining food quality and understand how traceability plays a key role in ensuring freshness from farm to fork.
What is Farm to Fork Freshness?
‘Farm to Fork’ refers to the complete journey of a food product, starting from when it is grown on a farm till it reaches the consumer’s plate, with a focus on preserving the freshness of the product at every stage. This underscores the importance of proper handling, storage conditions, and transportation to preserve flavour, quality, nutritional value, and safety.
The adoption and ultimately successful implementation of this concept play an important role in the entire supply chain management. This helps to ensure food’s original nutritional value remains unaffected and that the food we consume is not only healthy and tasty but also safe. Food quality is best preserved only when there is less time between harvest and consumption. To ensure this, traceability plays an important role by helping track the complete journey and identifying complications at the earliest. Barcodes facilitate this traceability from farm to fork. Let’s first understand what barcodes are, their importance and how they play a role in streamlining the food supply chain.
The Role of Barcodes in the Industry
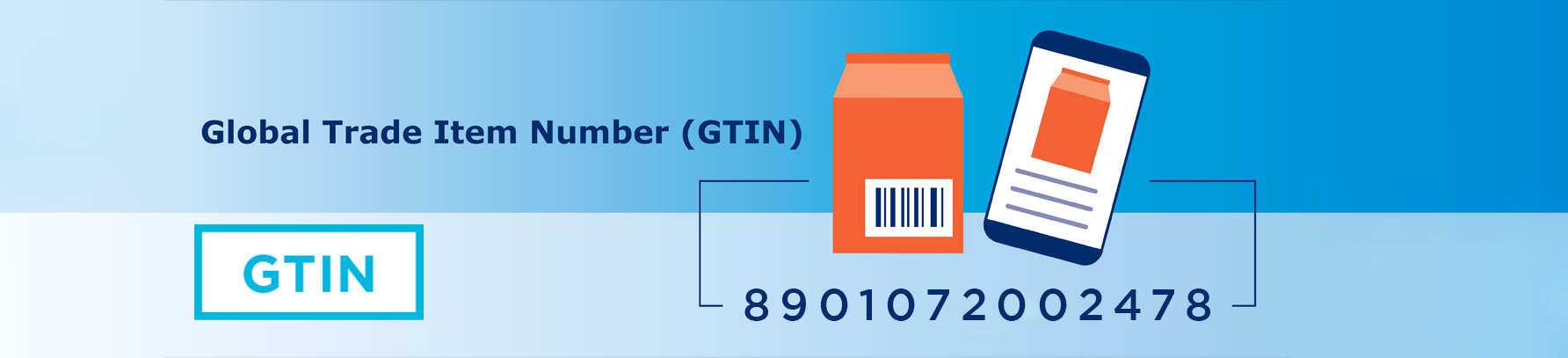
Barcodes are machine-readable representations of data. They can either be one-dimensional (1D) or two-dimensional (2D). Barcodes contain a unique identification number called the GTIN (Global Trade Item Number), which helps uniquely identify every product or Stock-keeping unit (SKU) being traded. The GTIN is composed of four components – Country Prefix, Company Code, Product Code and Check Digit. Find below the function of each of them –
- Country Code— A country code is a prefix allotted by GS1 Global to the member organisation. India has ‘890’ as its country prefix.
- Company Code – Company code is allotted by GS1 member organisations to identify the company registered for barcodes uniquely. Country code and company code together form the Global Company Prefix (GCP).
- Product Code—A product code is a unique identifier for a specific product or item, used to distinguish it from other products in a catalogue or inventory system. It enables efficient tracking, management, and classification of goods within supply chains.
- Check Digit: The check digit is a calculated number that is appended to a series of digits (like a barcode or identification number) to verify the accuracy of the entire number. It helps detect errors in data entry, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the product identification system.
Barcodes serve as a key tool in the supply chain as they provide a quick and accurate method of tracking and tracing the complete journey of products with a simple scan. Below are some reasons for how they help –
- Automated Data Capture – Barcodes can be scanned via hand-held scanners, machine readers, and smartphones (in the case of 2D barcodes), automating the data capture process. This automatic data capture also mitigates errors caused by manual data entry.
- Real-time Information—Barcodes give every supply chain stakeholder access to authentic, real-time information throughout the product’s journey. Upon scanning, you can access product data on manufacturing details, price, expiry date, etc., simplifying the decision-making process.
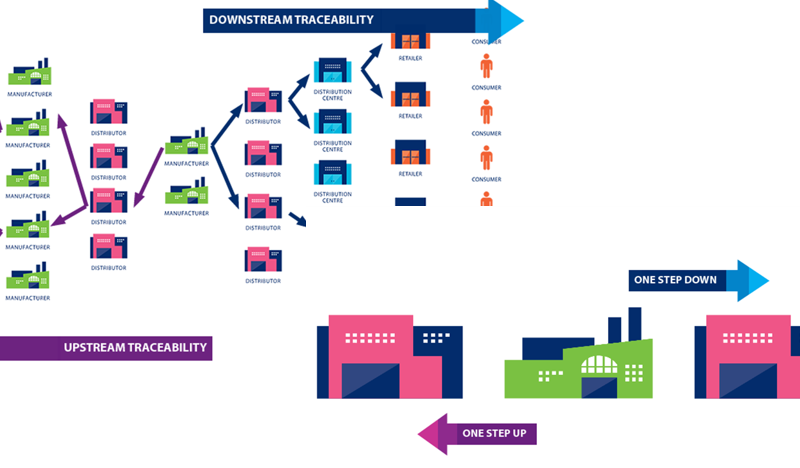
- Improved Visibility – Businesses can have end-to-end visibility of product flows. For example, if a product is recalled or has an issue, barcodes make it easy to trace every affected item throughout the system, even down to the individual unit.
- Regulatory Compliance – Regulatory requirements often demand traceability in industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and logistics. Barcodes help businesses comply with these regulations by enabling them to meet regulatory requirements.
- Enhancing Order Fulfilment – Barcodes play an important role in ensuring quick and accurate identification of products in a warehouse, empowering staff to efficiently locate and ship products to the concerned customers or stores.
Exercise Precautions before Purchasing Barcodes
GS1 barcodes are the only authorised barcodes across the globe. No other barcodes can provide the same interoperability, structure, and standardisation required for global trade except GS1 barcodes. GS1 India is the only organisation authorised to issue barcodes (starting with ‘890’) to companies in India; no other organisation is authorised to issue barcodes starting with ‘890’. Companies must stay vigilant and purchase ‘890’ barcodes from GS1 member organisations only.
Farm to Fork Traceability in the Indian Army
With their ability to facilitate traceability, GS1 barcodes play a vital role in ensuring transparency throughout the product’s farm-to-fork journey. Let’s understand the role of barcodes in facilitating traceability and guaranteeing food freshness with the example of the Indian Army Food Traceability (IAFT) project.
About IAFT
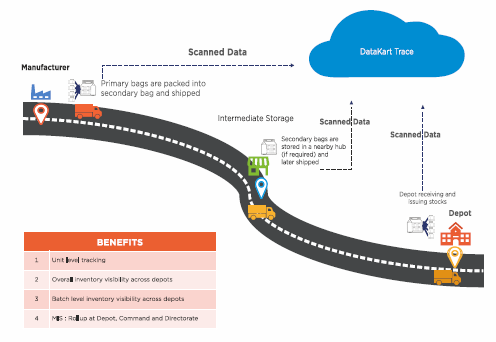
IAFT is an initiative under which the Indian Army has leveraged GS1 standards to ensure that only quality and healthy food reaches soldiers. This initiative is based on the FSSAI recall and traceability guidelines. The Indian Army has directed its food suppliers to comply with DataKart Trace – a traceability solution provided by GS1 India.
How Does it Work?
With DataKart Trace, the Indian Army carries unit-level tracing and tracking of food supplies to the Indian Army. Every data related to the movement of army ration items in the supply chain gets traced with the scan of barcodes. The process begins with careful supplier selection, followed by storage and monitoring under optimal conditions, and ends with the delivery of food to military units, often in remote areas.
Outcomes Achieved
Here are some results achieved by the Indian Army with the implementation of GS1 barcodes and the adoption of a traceability solution –
- Increased food safety – Reduced risk of spoilage or contamination, and allowed for quick identification and resolution of any issues.
- Enhanced supply chain management – Promoted transparency and ensured accountability by documenting every stage of food handling.
- Availability of Healthy Food – Soldiers benefited from safe, nutritious, and high-quality food because of strengthened trust and efficiency in food handling and delivery.
Applications of GS1 Barcodes across the Supply Chain
GS1 barcodes benefit the entire supply chain by providing authentic and accurate product information at every stage.
Here’s how each stakeholder benefits from GS1 barcodes –
- Farmers: QR codes, a type of 2D barcode, are present on pesticides and insecticides, ensuring farmers receive genuine and quality products to harvest crops.
- Transporters: SSCC (Serial Shipping Container Code), a type of 1D barcode, is applied to shipping containers/pallets to identify and track the products throughout the product’s supply chain journey. Unlike the standard 1D barcodes, SSCC can contain more information, such as expiry date, manufacturing details, batch/lot number, etc.
- Retailers: At point-of-sale, barcodes help streamline inventory management and help retailers follow sustainability and waste reduction practices by promoting the First Expiry, First Out (FEFO) principle.
- Consumers: With the Smart Consumer app, consumers can scan the product’s barcode (in case of 2D) and get detailed insights on products they wish to buy. They can also list the product’s GTIN on the ‘Verified by GS1’’ page to validate product details, empowering them to make smarter and more informed decisions.
Conclusion
With industries transitioning to 2D barcodes, the adoption of traceability measures will improve and escalate. With just a simple scan using a smartphone, stakeholders will be able to get information on the entire product’s lifecycle. People will be able to fetch information on how and when the product was manufactured, promoting better decision-making. To get authorised barcodes, companies can get registered with GS1 India, or simply click this link here – https://www.gs1india.org/content/get-a-barcode/
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What is food traceability, and why is it important?
Food traceability refers to tracking the complete journey of food products from manufacturing to the final product reaching the consumers.
2. How do GS1 barcodes support farm-to-fork traceability?
GS1 barcodes can be scanned and used at each supply chain level by the company to know the exact details about their products, thus promoting farm-to-fork traceability.
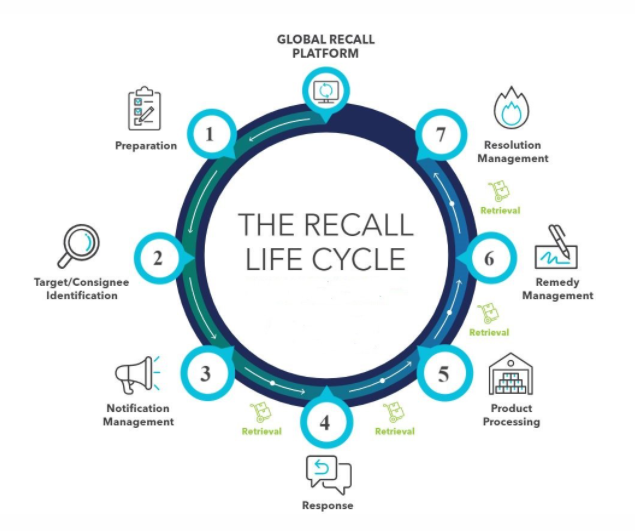
3. What is the role of GS1 standards in food product recalls?
GS1 barcodes can be scanned to identify supply chain issues at the earliest and take corrective measures.











.png)
.png)