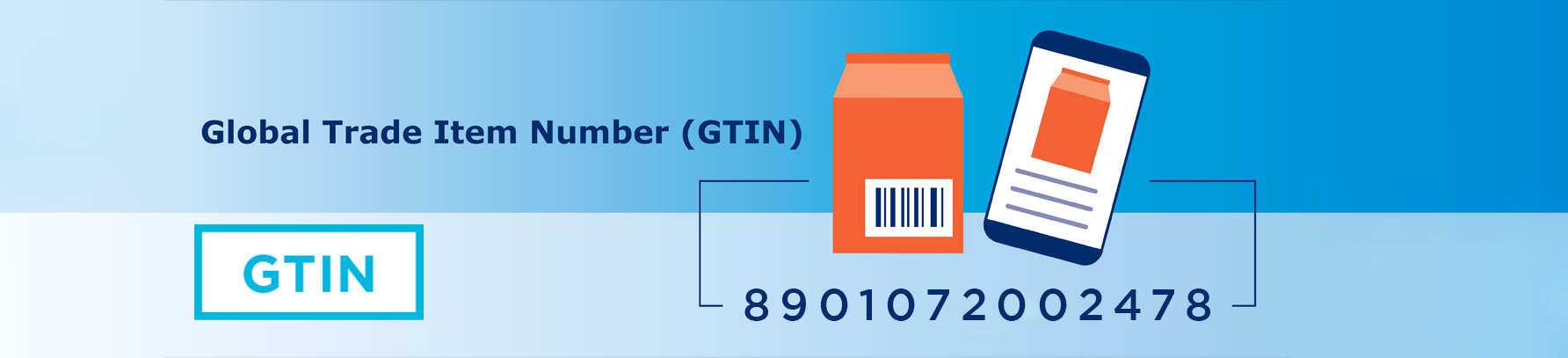
GTIN’s full form is Global Trade Item Number, a unique numerical identifier for products and services in the supply chain. The GTIN-14 barcode format specifically uses 14 digits to provide detailed information about an item, including its manufacturer and product type.
This system is designed to make identifying and tracking products easier and more efficient, no matter where they are in the world. By using GTIN-14 barcode, businesses can ensure that their products are correctly categorized, helping to streamline inventory management, checkout processes, and global trade operations.
This universal standard aids in reducing confusion and enhancing the accuracy of product information across various platforms and countries.
Importance of GTIN-14 Barcodes for Businesses
GTIN-14 barcodes play a crucial role in enhancing business operations across various sectors.
- Efficiency in Product Identification: GTIN-14 barcodes play a crucial role in the seamless identification of products across various platforms and databases. They ensure accurate tracking and identification, reducing the chances of errors and improving operational efficiency.
- Global Trade Compliance: For businesses engaged in international trade, GTIN-14 barcodes are essential for meeting global trade standards and regulations. They facilitate smoother customs clearance and compliance with international trade protocols, making cross-border transactions more straightforward.
- Inventory Management Streamlining: Utilizing GTIN-14 barcodes significantly enhances inventory management processes. They enable precise tracking of stock levels, help in forecasting demand, and streamline the replenishment process, thus minimising stockouts and overstock situations.
Overview of GTIN-14 Structure
The GTIN-14 structure is a system designed to facilitate global trade and supply chain management by providing a universal standard for product identification. This system is particularly beneficial for businesses as it helps in efficiently managing inventory, tracking products throughout the supply chain, and ensuring compliance with global trade regulations.
A GTIN-14 is composed of four main components:
- Indicator Digit: This digit ranges from 1 to 8 and is used to identify different packaging levels within the product hierarchy, such as a single item or a case of items. The indicator digit “9” is reserved for variable measure products and is an integral part of GTIN-14, distinguishing it from other GTIN formats.
- GS1 Company Prefix: A unique sequence of numbers allocated to a company by a GS1 Member Organisation. This prefix is the backbone of the GTIN system, ensuring that each product identifier is globally unique. For GTIN-12, this is referred to as the UPC Company Prefix.
- Item Reference: Assigned by the company, this portion of the GTIN-14 serves to uniquely identify a specific product or SKU. The length of the Item Reference is inversely related to the length of the GS1 Company Prefix; a longer company prefix means a shorter item reference, and vice versa.
-
Check Digit: The final component of the GTIN-14, this single digit is calculated from the other digits in the GTIN. Its purpose is to ensure that the GTIN is properly composed, helping to prevent errors in data entry or scanning. The check digit is a critical part of the GTIN, ensuring data integrity across digital and physical tracking systems.
Together, these components create a GTIN-14 that uniquely identifies a product and its packaging hierarchy, facilitating efficient logistics, inventory management, and compliance with international standards.
Understanding GTIN-14 Encoding
GTIN-14 encoding is a method for creating a 14-digit number to uniquely identify products across the globe. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
- Company Prefix: This is a unique series of numbers given to companies by GS1 India. It helps identify who made or distributed the product.
- Item Reference: These numbers come after the company prefix and identify a specific product made by that company. This way, each product gets its own unique identifier.
- Check Digit: The final digit of a GTIN-14 is calculated based on the previous 13 digits. It’s used to double-check that the GTIN-14 is correct and hasn’t been misread or mistyped.
Differentiation between GTIN-14 and Other Barcodes
GTIN-14 barcodes are crucial in tracking products across various levels of packaging and throughout the global supply chain. Unlike GTIN-12 and GTIN-13, which are primarily used for identifying products at the consumer unit level (like a single item on a store shelf), GTIN-14 is designed to identify products at all packaging levels, including cases, cartons, or pallets. This makes GTIN-14 exceptionally versatile, providing a comprehensive solution for managing inventory across different stages of distribution and sales.
When compared to Universal Product Code (UPC) and European Article Number (EAN) barcodes, GTIN-14 offers a broader scope of application. UPC barcodes contain 12 digits, while EAN barcodes, prevalent in international markets, contain 13 digits. Both UPC and EAN are geared towards retail point-of-sale identification. In contrast, GTIN-14, with its additional capacity, extends beyond the retail environment to support efficient supply chain management from manufacturers to retailers, ensuring accurate tracking and handling of goods in bulk or individual units. This unique capability underscores the importance of GTIN-14 in global trade, enabling seamless product identification and compliance with international standards.
Benefits of Implementing GTIN-14 Barcodes
Implementing GTIN-14 barcodes brings significant advantages to businesses by making the supply chain more efficient. This system speeds up the process of identifying products accurately, saving time and reducing errors. With GTIN-14 barcodes, products are easier to track throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to final sale. This enhanced traceability not only helps in managing inventory better but also improves the ability to recall products quickly if needed. Overall, GTIN-14 barcodes streamline operations, ensuring products move smoothly and safely to their destinations, which can lead to happier customers and potentially increased sales for businesses.
Compliance with Global Standards
Complying with global standards is crucial for businesses to thrive in the international market. By adopting GTIN-14 barcodes, companies ensure their products meet the stringent requirements set by retailers worldwide. This not only boosts the efficiency of supply chain operations but also opens doors to a broader marketplace. Furthermore, GTIN-14 barcodes play a significant role in facilitating cross-border trade. They provide a universally recognised system that helps in the seamless movement of goods across different countries, minimising delays and simplifying customs procedures. This compliance enhances global trade opportunities, making it easier for businesses to expand their reach and participate in the global economy.
Troubleshooting and Common Challenges
-
Addressing Barcode Printing Issues: Sometimes, barcodes don’t print correctly. This can be due to low ink levels or incorrect printer settings. Make sure your printer is properly calibrated and has enough ink to ensure clear, crisp barcodes.
-
Ensuring Proper Resolution and Size: Barcodes must be the right size and resolution to scan correctly. Check that your barcode dimensions meet the standard requirements and that the resolution is high enough for scanners to read.
-
Troubleshooting Barcode Scanning Problems: If barcodes aren’t scanning, first check the scanner’s compatibility with GTIN-14 barcodes. Clean the scanner lens and ensure the barcode isn’t wrinkled or obscured by glare.
Handling Data Synchronization Challenges
-
Syncing GTIN-14 Data Across Platforms: To keep product data consistent across systems, regularly update all platforms with the latest GTIN-14 information. Use a centralised database to manage updates efficiently.
-
Resolving Discrepancies in Product Information: When product details don’t match across platforms, it can lead to confusion. Regularly audit your data to find and fix any discrepancies, ensuring all information is accurate and up-to-date.
Conclusion
Embracing GTIN-14 barcodes simplifies operations, enhances efficiency, and prepares businesses for global trade. Implementing these standards is not just about compliance but about leveraging technology to improve business practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does a GTIN-14 barcode differ from other types of barcodes?
GTIN-14 provides a unique identifier for various packaging levels, differentiating it from other barcode types.
2. Do I need a GTIN-14 barcode for every product variation?
Yes, each variation requires a unique GTIN-14 for accurate identification and tracking.
3. Can I use my existing UPC or EAN barcode instead of GTIN-14?
While UPC and EAN are acceptable in retail, GTIN-14 offers broader application across packaging levels.
4. How do I obtain a GS1 Company Prefix for generating GTIN-14 barcodes?
Registration with GS1 is the first step towards generating GTIN-14 barcodes.
5. Are there any specific requirements for printing GTIN-14 barcodes?
Adhering to GS1 specifications ensures barcodes are readable and compliant.
6. What should I do if I encounter scanning issues with GTIN-14 barcodes?
Regular verification and quality checks can prevent and resolve scanning problems.
7. Do all countries recognise GTIN-14 barcodes for cross-border trade?
GTIN-14 is globally recognised, facilitating international transactions.
8. Can I assign GTIN-14 barcodes to non-retail products?
GTIN-14 is versatile and suitable for both retail and non-retail products.
9. Are there any ongoing fees associated with using GTIN-14 barcodes?
While initial registration involves a fee, ongoing costs depend on GS1 membership and services utilised.